m6A Site Prediction
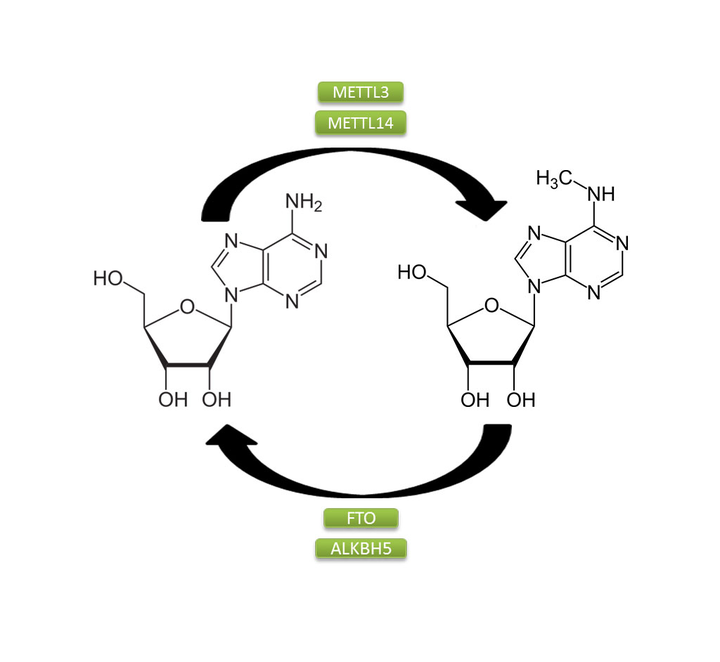
m6a stands for N6-methyladensine which a common RNA methylation modification. It plays an important role in interplay with microRNAs, alternative splicing, and also in translation efficiency. Experimental identification of this modification is costly and time-taking, hence it is imperative to design in-silico tools for the determination of this modification. A feature set consisting of the sequence motifs was developed. Multiple deep learning models were tested of which the residual network model outperformed the rest. The developed models were compared with Deepm6ASeq, a state-of-the-art deep learning model for the determination of m6a sites in a sequence. The tests on the three different species showed that the proposed residual network model had better precision than DeepM6ASeq. This model was used to detect m6A sites in the genome of SARS-CoV-2.